Unity in Data - Federated
Dataspace
In an era where solving societal challenges increasingly depends on high-quality data, governments across Europe are rethinking the way data is shared.
The Dutch Federated Data Space (FDS) offers a compelling example of how to responsibly unlock data across sectors and domains, while keeping control local and protecting public values.
Intergovernmental Data Strategy
introduction
The Dutch Federatief Datastelsel (FDS) is a federated data infrastructure developed under the national Intergovernmental Data Strategy (IBDS), enabling trusted and interoperable data sharing across public organisations.
IBDS Data Strategy
Most of the foundational documentation and guidance about the Federated Data Space and strategy can be found on realisatieibds.nl — the official portal of the Dutch data strategy. Please note: the website is in Dutch.IBDS is a national programme in the Netherlands aimed at enabling responsible and effective data use across all levels of government — municipalities, provinces, water boards, agencies, and central ministries. The strategy focuses on public value, interoperability, and trust, and the FDS is one of its key implementation tracks.It's closely related to the broader Dutch NDS Digital Strategy.
Federated Data Space
The FDS is not a centralized system. Instead, it connects data providers and users through a shared set of agreements, standards and governance functions. Its core principles — such as data sovereignty, minimal data exchange, and federation — align closely with European ambitions for interoperable, cross-border data spaces as outlined in the Interoperable Europe Act and European Data Strategy.The FDS illustrates how a national initiative can be a building block in a broader European data ecosystem. With its focus on federation, trust, and public value, it invites other countries to join forces and co-create a future where data truly works for society.
Why it matters for Europe
Interoperability at scale: FDS builds on semantic and technical interoperability standards like REST API, DCAT, and FSC, making it easier to connect with EU-wide initiatives such as SIMPL.Decentral trust and control: Through federated access and audit mechanisms (e.g., FTV, LDV), the FDS safeguards privacy and accountability — crucial for compliance with the GDPR and future cross-border services.Collaborative innovation: The FDS includes a simulation environment and Digilab, where public organisations co-develop and test solutions. This iterative, open-source model mirrors the co-creation approach of the EU's Digital Europe Programme.European relevance: As member states move toward interoperable government and data spaces, the FDS shows how such systems can be designed for resilience, public value, and collaboration. It is already applied in sectors like taxation, mobility, and social care, with pioneers such as CBS, Kadaster, and the Dutch Chamber of Commerce contributing to its growth.The FDS illustrates how a national initiative can be a building block in a broader European data ecosystem. With its focus on federation, trust, and public value, it invites other countries to join forces and co-create a future where data truly works for society.
Interoperability
Interoperability is a cornerstone of the Federated Data System (FDS), ensuring that data can flow seamlessly across organizational and sectoral boundaries. Within the Netherlands, the FDS builds on the foundations of the Generic Digital Infrastructure (GDI), the national digital infrastructure that provides common facilities for identification, messaging, and data exchange.By aligning with GDI principles and integrating open standards the FDS enables public organisations to connect their data systems without centralising control. This approach fosters cross-domain collaboration while preserving autonomy and compliance, making it easier to share, reuse, and trust data across the public sector.The GDI and the Dataspace Connector (DSC, developed under IDSA) both aim to support secure and interoperable data exchange, but they operate at different levels and with distinct scopes. The GDI contains a more detailed approach to interoperability.The Dutch FDS leverages GDI components as foundational national infrastructure, while also exploring compatibility with European dataspace technologies like the DSC.The website federatief.datastelsel.nl is the collaborative workspace for developing the Dutch Federated Data System (FDS). It offers technical and governance documentation, co-created by public organisations and experts working on data interoperability and shared standards.
Dutch national data
DATA
data.overheid.nl is the Dutch national data portal, providing the overview of thousands of datasets published by public organisations. It promotes transparency, innovation, and reuse of government data by making metadata and APIs findable, searchable, and accessible to citizens, developers, and businesses.
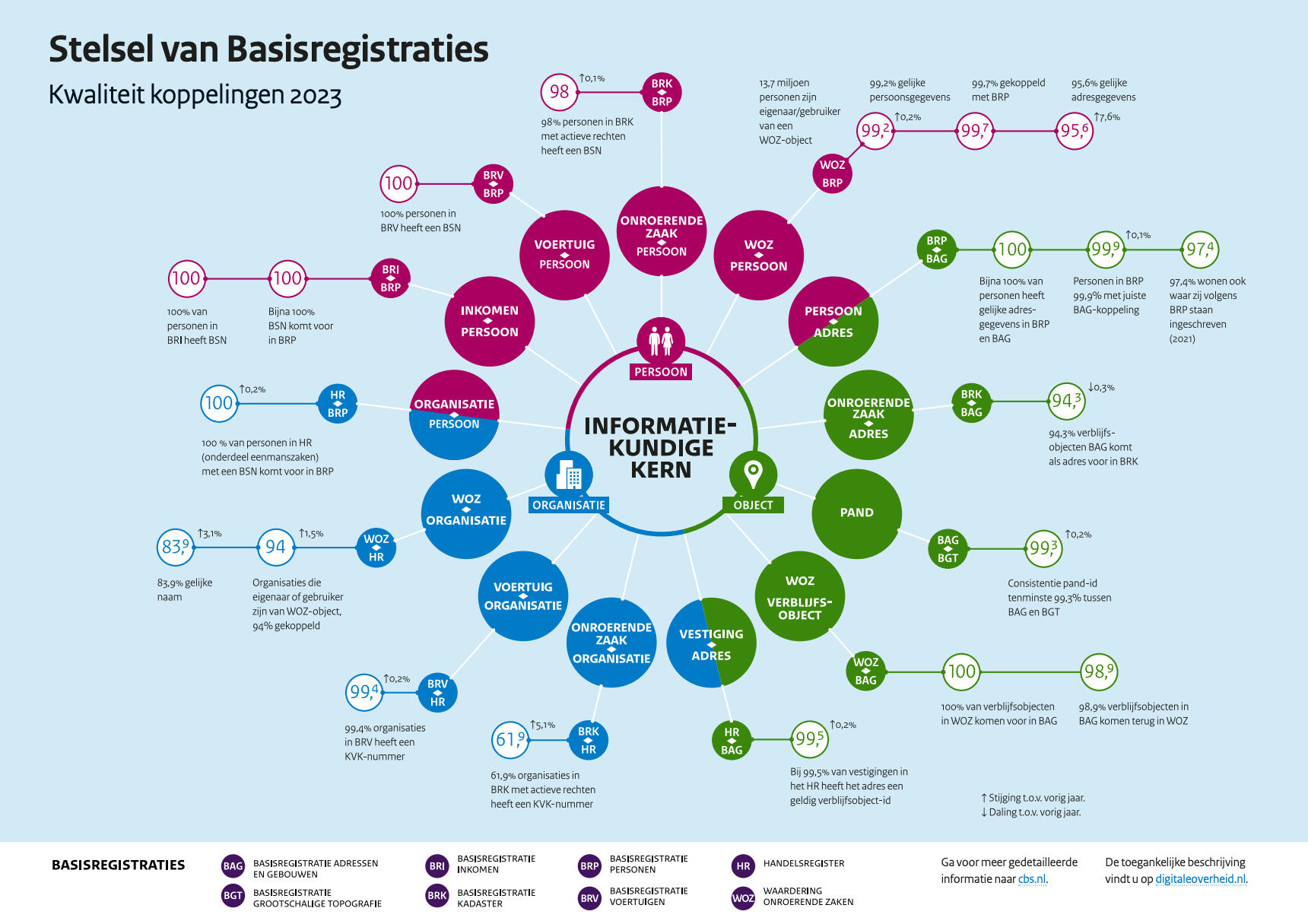
The Dutch Federated Data Space
More?
This page offers a brief English introduction to the Dutch Federated Data System (FDS). For a deeper dive into the architecture, governance, and practical tools, you may want to explore the full documentation — most of which is available in Dutch.
Unidat.eu